Architecture of ST4SD Cloud
ST4SD is a cloud native, but not cloud exclusive, framework. When you install the toolkit on the cloud you deploy a collection of microservices. The microservices are acting as the proxy between the user and the core runtime system of ST4SD.
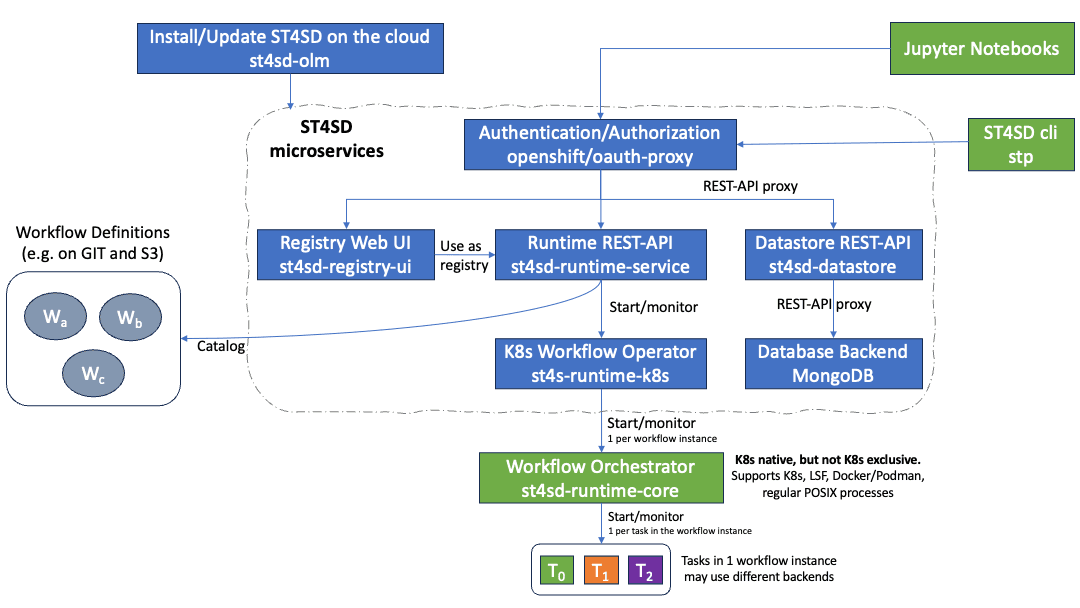
Users interact with the microservices using Jupyter Notebooks and the Command Line Interface (CLI) of ST4SD stp.
The definitions of virtual experiments live on a server for example a Git server or a Cloud Object Storage server like S3. The Runtime REST-API and the registry web ui contain pointers to the virtual experiment definitions which we term Parameterised Virtual Experiment Packages.
Users interact with the Runtime REST-API to run parameterised virtual experiments packages. The Runtime Service creates a Workflow CustomResource which triggers the K8s Workflow Operator. The K8s Workflow Operator creates a main pod that handles the orchestration of the virtual experiment instance using the Workflow Orchestrator. The Workflow Orchestrator may launch minion pods for the tasks of components in the virtual experiment that use the kubernetes backend of ST4SD.
Users can also run ST4SD on a machine that is not part of the cloud. For example, they may install the Workflow Orchestrator on the login node of a High Performance Cluster or their personal laptop. That will enable them to execute virtual experiments that use other backends of ST4SD, such as lsf, docker, and local (i.e. regular POSIX processes).